Qt 程序示例与范式总结
大约 10 分钟
Qt 程序示例与范式总结
基础使用
范式总结
- 信号槽机制
- 变量监听方法参见枚举量绑定按钮组
- 应当将被监听变量设为私有, 并定义访问方法, 修改槽函数, 监听信号
- 以
None声明变量, 并在最后通过槽函数赋初值 - 与组件行为绑定时, 还需要定义对应的私有槽函数, 并在修改变量的同时更新组件
- 在修改槽函数中, 应当包含
- 判断是否为真修改 (新旧值是否相同)
- 修改原始变量
- 发出信号
- 同步与变量绑定的子组件
- 信号槽连接方法
- 首先即通过信号实例的
connect方法建立连接 - 在连接后应当通过发出信号组件的有关方法定义初值 (不必担心重复初始化, 无论何种层级的组件都应当有此操作)
- 首先即通过信号实例的
- 变量监听方法参见枚举量绑定按钮组
- 组件构建
- 自定义组件区的构造函数内容
- 调用基类构造函数
- 对输入参数进行初步处理
- 定义所有子组件并在定义后设置基本样式
- 组件布局
- 从底层级向高层级布局 (如果复杂则应拆分为自定义组件区)
- 布局先定义布局引擎, 再插入组件, 最后设置布局引擎
- 调用
setLayout使布局生效
- 各个子组件之间的信号槽连接, 并设置组件的初值
- 组件初始化设置
- 自定义组件区的构造函数内容
- 命名规范
- 子组件以及相应数据结构命名
- 使用小写开头, 大写区分间隔
- Qt 原生组件或自定义实用组件使用缩写 (名称前两个单词首字母) + 功能组合作为成员名 (结合 IDE, 快速定位组件)
- 自定义组件区使用全称作为成员名
- 组件方法命名 (包括信号)
- 使用大写开头, 大写区分间隔 (与继承的原生组件方法区分)
- 槽方法以
Set开头, 信号以名词开头, 一般方法以动词开头
- 其他
- 与组件无直接关系的成员与方法实用小写字母, 下划线区分间隔 (与 Python 标准一致)
- 布局引擎同组件, 但使用
layout为开头, 后接功能
- 子组件以及相应数据结构命名
枚举量绑定按钮组
from PySide6.QtCore import Slot, Signal
from PySide6.QtWidgets import (
QApplication, QWidget, QRadioButton, QButtonGroup, QAbstractButton,
QBoxLayout, QLabel,
)
from enum import Enum
from typing import Union, Sequence, Optional, Iterable, Any
class Color(Enum):
Red = 0
Green = 1
Blue = 2
Yellow = 3
ColorName = {
Color.Red: "红",
Color.Green: "绿",
Color.Blue: "蓝",
Color.Yellow: "黄"
}
# 实用类, 当需要将按钮组与枚举量相绑定时, 可参考此类型的实现
class ValueBindButtonGroup(QButtonGroup):
'''
根据枚举类型信息, 生成对应的复选框按钮组组件
'''
def __init__(self, bind_enum: type, default_value: object, name_list: Optional[Union[dict[Any, str], Sequence[str]]] = None, button_widget: type = QRadioButton) -> None:
'''
* `bind_enum` 继承自 enum.Enum 类的枚举类型
* `default_value` 默认选中值
* `name_list` 按钮名称列表, 默认使用枚举类型的键名
* `button_widget` 按钮组件类型, 默认使用 `QRadioButton`
'''
super().__init__()
self._button_map: dict[object, QAbstractButton] = {}
self._bind_enum = bind_enum
self._enum_values = tuple(self._bind_enum.__members__.values())
# 生成按钮并绑定
if name_list == None:
name_list = tuple(bind_enum.__members__.keys())
elif isinstance(name_list, dict):
name_list = tuple(name_list[key] for key in self._enum_values)
for id, (key, value) in enumerate(zip(name_list, self._enum_values)):
self._button_map[value] = button_widget(str(key))
self._button_map[value].setCheckable(True)
self.addButton(self._button_map[value], id)
# 首先对被监控变量取空值, 并设为私有
self._value = None
# 使用私有槽, 将变量绑定到按钮组的结果上 (还需要反向绑定, 具体见下)
self.idClicked.connect(self._SetValueByButton)
# 通过给定方法, 给被监控变量赋初值
self.SetValue(default_value)
def value(self):
'''
获取当前选中值
'''
return self._value
ValueChange = Signal(object)
@Slot(object)
def SetValue(self, new_value):
'''
设置当前选中值
'''
# 仅当变量与原先不同时, 属于一次有效的修改
if new_value != self._value:
if not isinstance(new_value, self._bind_enum):
raise(Exception(f"Require Type {self._bind_enum} But Given {type(new_value)} Instead"))
self._value = new_value
# 通过信号监控变量改变
self.ValueChange.emit(new_value)
# 在修改函数中, 将按钮组反向绑定到按钮上
self._button_map[new_value].click()
@Slot(int)
def _SetValueByButton(self, id):
'''
私有组件绑定槽
'''
new_value = self._enum_values[id]
# 与 Clicked 信号绑定, 因此重复点击也肯能触发
if new_value != self._value:
self._value = new_value
self.ValueChange.emit(new_value)
def GetButton(self, value: object) -> QAbstractButton:
'''
获取枚举值对应的组件对象
'''
if not isinstance(value, self._bind_enum):
raise(Exception(f"Require Type {self._bind_enum} But Given {type(value)} Instead"))
return self._button_map[value]
def IteratorButton(self) -> Iterable[tuple[object, QAbstractButton]]:
'''
获取按钮组件映射的迭代器
'''
return self._button_map.items()
class MainWindow(QWidget):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
# 创建组件
self.vbInput = ValueBindButtonGroup(Color, Color.Red, ColorName)
self.lView = QLabel("选择颜色:")
# 组件布局
# 从底至上布局, 如果过于复杂, 应当拆分为多个容器类
self.layout_group = QBoxLayout(QBoxLayout.Direction.LeftToRight)
for (value, button) in self.vbInput.IteratorButton():
self.layout_group.addWidget(button)
self.layout_base = QBoxLayout(QBoxLayout.Direction.TopToBottom)
self.layout_base.addLayout(self.layout_group)
self.layout_base.addWidget(self.lView)
self.setLayout(self.layout_base)
# 建立连接, 并使用被链接量的初值 (被链接量已初始化) , 调用槽函数完成初始化
self.vbInput.ValueChange.connect(self.SelectColor)
self.SelectColor(self.vbInput.value())
@Slot(Color)
def SelectColor(self, color):
self.lView.setText(f"当前选择颜色: {ColorName[color]}")
app = QApplication()
win = MainWindow()
win.show()
app.exec()
运行效果 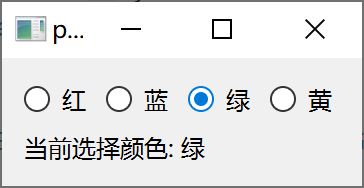
文本输入渲染程序
from PySide6.QtCore import Slot, Signal
from PySide6.QtWidgets import (
QApplication, QWidget, QTextEdit, QTextBrowser, QPushButton, QRadioButton, QButtonGroup, QLabel, QAbstractButton,
QBoxLayout,
QSizePolicy
)
from enum import Enum
from typing import Optional, Sequence, Iterable
class RenderMode(Enum):
HTML = 0
MARKDOWN = 1
class ValueBindButtonGroup(QButtonGroup):
... # 具体见枚举量绑定按钮组
class InputArea(QWidget):
'''
输出区
'''
updateText = Signal(str)
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.teInput = QTextEdit()
self.teInput.setPlaceholderText("输入内容")
self.layoutBase = QBoxLayout(QBoxLayout.Direction.TopToBottom)
self.layoutBase.addWidget(QLabel("输入区"))
self.layoutBase.addWidget(self.teInput)
self.setLayout(self.layoutBase)
self.teInput.textChanged.connect(lambda: self.updateText.emit(self.teInput.toPlainText()))
self.teInput.setPlainText("")
class RenderArea(QWidget):
'''
渲染显示区
'''
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.tbRender = QTextBrowser()
self.layoutBase = QBoxLayout(QBoxLayout.Direction.TopToBottom)
self.layoutBase.addWidget(QLabel("渲染区"))
self.layoutBase.addWidget(self.tbRender)
self.setLayout(self.layoutBase)
self.renderMode = None
self.SetRenderMode(RenderMode.HTML)
self.SetRenderText("")
@Slot(RenderMode)
def SetRenderMode(self, mode):
if self.renderMode != mode:
self.renderMode = mode
self.SetRenderText(self.tbRender.toPlainText())
@Slot(str)
def SetRenderText(self, text):
if self.renderMode == RenderMode.HTML:
self.tbRender.setHtml(text)
elif self.renderMode == RenderMode.MARKDOWN:
self.tbRender.setMarkdown(text)
else:
self.tbRender.setHtml("<font color='red'>Unknown Render Mode</font>")
class MainArea(QWidget):
'''
程序主要区域
'''
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.inputArea = InputArea()
self.renderArea = RenderArea()
self.layoutBase = QBoxLayout(QBoxLayout.Direction.LeftToRight)
self.layoutBase.addWidget(self.inputArea)
self.layoutBase.addWidget(self.renderArea)
self.setLayout(self.layoutBase)
self.inputArea.updateText.connect(self.renderArea.SetRenderText)
self.inputArea.teInput.setPlainText("")
class ControlArea(QWidget):
'''
程序控制区域
'''
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.pbClear = QPushButton("清除内容")
self.vbMode = ValueBindButtonGroup(RenderMode, RenderMode.HTML)
self.layoutBase = QBoxLayout(QBoxLayout.Direction.LeftToRight)
self.layoutBase.addWidget(self.pbClear)
self.layoutBase.addWidget(QLabel("渲染模式:"))
self.layoutBase.addWidget(self.vbMode.GetButton(RenderMode.HTML))
self.layoutBase.addWidget(self.vbMode.GetButton(RenderMode.MARKDOWN))
self.setLayout(self.layoutBase)
self.setSizePolicy(QSizePolicy.Policy.Fixed, QSizePolicy.Policy.Minimum)
class MainApp(QWidget):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.controlArea = ControlArea()
self.mainArea = MainArea()
self.layoutBase = QBoxLayout(QBoxLayout.Direction.TopToBottom)
self.layoutBase.addWidget(self.mainArea)
self.layoutBase.addWidget(self.controlArea)
self.setLayout(self.layoutBase)
self.controlArea.vbMode.ValueChange.connect(self.mainArea.renderArea.SetRenderMode)
self.controlArea.vbMode.SetValue(RenderMode.MARKDOWN)
self.controlArea.pbClear.clicked.connect(self.mainArea.inputArea.teInput.clear)
app = QApplication()
win = MainApp()
win.show()
app.exec()
运行效果 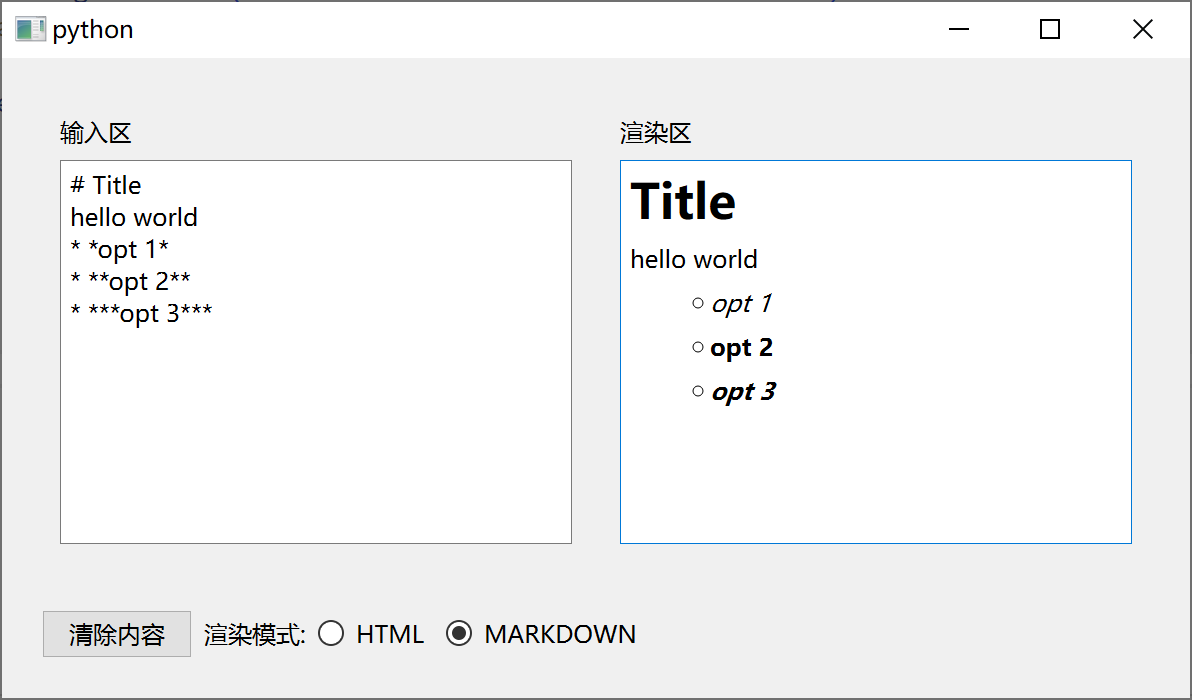
登录会话程序
from PySide6.QtCore import (
Slot, Signal
)
from PySide6.QtWidgets import (
QApplication,
QPushButton, QLabel, QLineEdit,
QDialogButtonBox,
QFormLayout, QBoxLayout,
QDialog, QWidget
)
from PySide6.QtGui import(
QRegularExpressionValidator, QValidator, QPixmap, QPalette
)
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass
class FormData:
account: str = ""
pw: str = ""
# 5 - 16 位数字
RE_ACCOUNT = r"^\d{5,16}$"
# 数字, 字母与特殊符号, 至少包含一个大写字母, 小写字母与数字, 8 - 20 位
RE_PW = r"^(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[A-Z])(?=.*\d)[a-zA-Z\d$@$!%*?&]{8,20}$"
# 使用信号监控验证是否通过
class ValidLineEdit(QLineEdit):
'''
实现验证信号 ValidStateChange 的输入栏组件
'''
ValidStateChange = Signal(bool)
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self._is_valid = None
self._SetValidState(False)
self.textChanged.connect(self._SlotCheckValid)
def is_valid(self):
return self._is_valid
@Slot()
def _SetValidState(self, is_valid):
if self._is_valid != is_valid:
self._is_valid = is_valid
self.ValidStateChange.emit(self._is_valid)
@Slot()
def _SlotCheckValid(self):
self._SetValidState(self.hasAcceptableInput())
# 通过继承布局的方式创建有关联的几个组件
class LineEditWithSignLayout(QBoxLayout):
'''
带有验证标识的输入栏布局
'''
# 图标路径
# https://uxwing.com/green-checkmark-line-icon/
YES_SIGN_PATH = "res/yes.svg"
# https://uxwing.com/red-x-line-icon/
NO_SIGN_PATH = "res/no.svg"
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(QBoxLayout.Direction.LeftToRight)
self.label = QLabel(" ")
self.label.setVisible(False)
self.lineEdit = ValidLineEdit()
self.addWidget(self.lineEdit)
self.addWidget(self.label)
# self.setLayout(self.layoutBase)
font_size = int(self.lineEdit.font().pointSize() * 2)
self.pmYes = QPixmap(self.YES_SIGN_PATH).scaled(font_size, font_size)
self.pmNo = QPixmap(self.NO_SIGN_PATH).scaled(font_size, font_size)
self.lineEdit.ValidStateChange.connect(self._SlotSetSign)
self._SlotSetSign(self.lineEdit.is_valid())
@Slot(object)
def _SlotSetSign(self, is_valid):
self.label.setVisible(True)
if is_valid:
self.label.setPixmap(self.pmYes)
else:
self.label.setPixmap(self.pmNo)
# 自定义验证器
class ValidatorImitator(QValidator):
'''
模仿已有输入栏的验证器
'''
def __init__(self, leObserved: QLineEdit) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.leObserved = leObserved
def validate(self, arg__1, arg__2):
res = None
if arg__1 == self.leObserved.text():
# 当内容与被模仿验证器相同时通过验证
res = QValidator.State.Acceptable
else:
# 一般情况下, 使用被模仿验证器判断输入是否合法
validator = self.leObserved.validator()
if validator == None:
res = QValidator.State.Intermediate
else:
if validator.validate(arg__1, arg__2)[0] != QValidator.State.Invalid: # type: ignore
res = QValidator.State.Intermediate
else:
res = QValidator.State.Invalid
return (res, arg__1, arg__2)
# 复杂会话窗口
class RegistDialog(QDialog):
def __init__(self, parent: QWidget) -> None:
super().__init__(parent)
# 表单收集数据
self._form_result = None
# 账号输入栏
lewsAccountInput = LineEditWithSignLayout()
self.leAccountInput = lewsAccountInput.lineEdit
self.leAccountInput.setPlaceholderText("输入账号")
self.leAccountInput.setValidator(
QRegularExpressionValidator(RE_ACCOUNT)
)
self.leAccountInput.setToolTip("账号为 5 - 16 位数字")
# 密码输入栏
lewsPwInput = LineEditWithSignLayout()
self.lePwInput = lewsPwInput.lineEdit
self.lePwInput.setPlaceholderText("输入密码")
self.lePwInput.setValidator(
QRegularExpressionValidator(RE_PW)
)
self.lePwInput.setEchoMode(
QLineEdit.EchoMode.Password
)
self.lePwInput.setToolTip("密码为数字, 字母与特殊符号的组合, 至少包含一个大写字母, 小写字母与数字, 8 - 20 位")
# 根据输入字符长度, 预留空间
font_width = self.lePwInput.font().pointSize()
self.lePwInput.setMinimumWidth(font_width * 30)
# 再次输入密码
lewsPwPardon = LineEditWithSignLayout()
self.lePwPardon = lewsPwPardon.lineEdit
self.lePwPardon.setPlaceholderText("再次输入密码")
self.lePwPardon.setValidator(
ValidatorImitator(self.lePwInput)
)
self.lePwPardon.setEchoMode(
QLineEdit.EchoMode.Password
)
self.lePwPardon.setToolTip("密码为数字, 字母与特殊符号的组合, 至少包含一个大写字母, 小写字母与数字, 8 - 20 位")
# 根据输入字符长度, 预留空间
font_width = self.lePwInput.font().pointSize()
self.lePwInput.setMinimumWidth(font_width * 30)
# 会话按钮
self.dbbButton = QDialogButtonBox()
self.dbbButton.setStandardButtons(
QDialogButtonBox.StandardButton.Ok |
QDialogButtonBox.StandardButton.Cancel
)
self.dbbButton.button(QDialogButtonBox.StandardButton.Ok).setText("确认")
self.dbbButton.button(QDialogButtonBox.StandardButton.Cancel).setText("取消")
self.dbbButton.accepted.connect(self.SlotOKCheck)
self.dbbButton.rejected.connect(self.reject)
# 警告标签
self.lWarn = QLabel(" ")
# 设置标签字体颜色
lWarnPalette = QPalette()
lWarnPalette.setColor(QPalette.ColorRole.WindowText, "#FF0000")
self.lWarn.setPalette(lWarnPalette)
# 布局
self.baseLayout = QFormLayout()
self.baseLayout.addRow(QLabel("注册账号"))
self.baseLayout.addRow("账号:", lewsAccountInput)
self.baseLayout.addRow("密码:", lewsPwInput)
self.baseLayout.addRow("确认密码:", lewsPwPardon)
self.baseLayout.addRow(self.lWarn)
self.baseLayout.addRow(self.dbbButton)
self.setLayout(self.baseLayout)
# 连接
# 用于退出时清空已有数据, 无论是否接收
self.finished.connect(self.ClearForm)
# 在用户提交前, 对输入内容进行检查
@Slot()
def SlotOKCheck(self):
if not self.leAccountInput.is_valid():
self.lWarn.setText("账号不正确")
elif not self.lePwInput.is_valid():
self.lWarn.setText("密码不满足要求")
elif not self.lePwPardon.is_valid():
self.lWarn.setText("重复输入密码不相同")
else:
# 通过检查后, 收集表单数据, 并退出会话
self._form_result = FormData(
account = self.leAccountInput.text(),
pw = self.lePwInput.text()
)
self.accept()
def get_form_result(self):
return self._form_result
@Slot()
def ClearForm(self):
'''
清空表单
'''
self.leAccountInput.clear()
self.lePwInput.clear()
self.lePwPardon.clear()
self._form_result = None
class MainWin(QWidget):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.dRegistForm = RegistDialog(self)
self.pbRegiste = QPushButton("注册")
self.lAccountInfo = QLabel("")
self.lPwInfo = QLabel("")
font_width = self.lPwInfo.font().pointSize()
self.lPwInfo.setMinimumWidth(font_width * 30)
self.layoutBase = QFormLayout()
self.layoutBase.addRow(self.pbRegiste)
self.layoutBase.addRow("注册账号:", self.lAccountInfo)
self.layoutBase.addRow("注册密码:", self.lPwInfo)
self.setLayout(self.layoutBase)
self.dRegistForm.accepted.connect(self._SlotDialogAccept)
self.pbRegiste.clicked.connect(self.dRegistForm.open)
@Slot()
def _SlotDialogAccept(self):
res = self.dRegistForm.get_form_result()
if res != None:
self.lAccountInfo.setText(res.account)
self.lPwInfo.setText(res.pw)
app = QApplication()
win = MainWin()
win.show()
app.exec()
运行效果 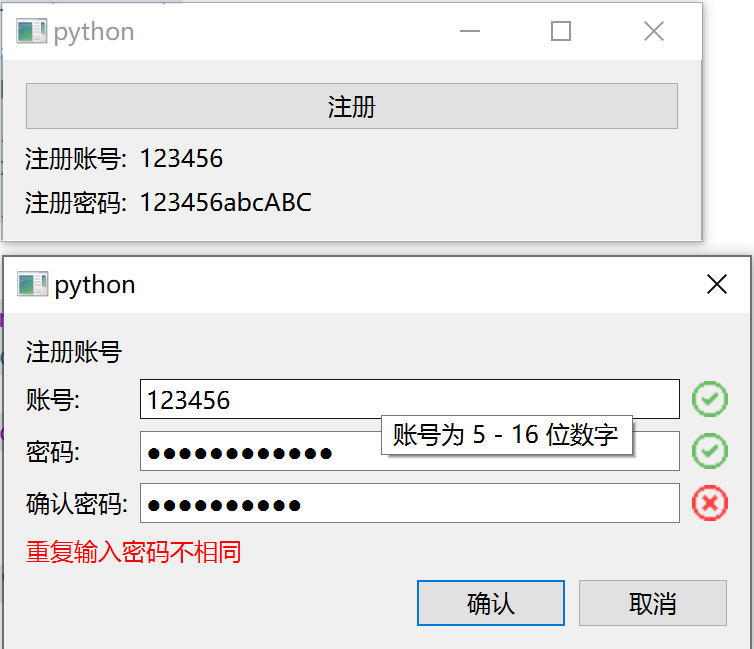
子进程管理程序
主程序
from PySide6.QtGui import QCloseEvent
from PySide6.QtWidgets import (
QWidget, QApplication,
QPushButton, QPlainTextEdit, QBoxLayout, QProgressBar
)
from PySide6.QtCore import (
QProcess, Slot
)
import time, warnings, re
# 匹配子进程关于进度的输出
progress_re = re.compile(r"task progress: ([.\d]+)%")
def progress_parser(output):
m = progress_re.search(output)
if m != None:
return int(float(m.group(1)))
else:
return None
class MainWin(QWidget):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.pbExecute = QPushButton("Execute")
self.pbExecute.clicked.connect(self.OnExecuteProcess)
self.pbTerminate = QPushButton("Terminate")
self.pbTerminate.clicked.connect(self.OnTerminateProcess)
self.pbTerminate.setEnabled(False)
self.progressBar = QProgressBar()
self.progressBar.setRange(0, 100)
self.progressBar.reset()
self.teOutput = QPlainTextEdit()
self.teOutput.setReadOnly(True)
self.p = None
self.layoutButtons = QBoxLayout(QBoxLayout.Direction.LeftToRight)
self.layoutButtons.addWidget(self.pbExecute)
self.layoutButtons.addWidget(self.pbTerminate)
self.layoutBase = QBoxLayout(QBoxLayout.Direction.TopToBottom)
self.layoutBase.addLayout(self.layoutButtons)
self.layoutBase.addWidget(self.progressBar)
self.layoutBase.addWidget(self.teOutput)
self.setLayout(self.layoutBase)
def closeEvent(self, event: QCloseEvent) -> None:
'''
窗口关闭事件
'''
# 当窗口关闭时, 向子进程发出关闭信息, 让其保存数据
if self.p != None:
self.p.kill()
self.p.waitForFinished()
# 由于子进程每次运行后都要销毁, 可以通过一个方法专门用于创建与设置子进程
def _CreateProcess(self, task_arg1):
'''
创建子进程对象
'''
p = QProcess(self)
p.setProgram("python")
# 将所有命令行参数转为字符串
p.setArguments(("test_process.py", str(task_arg1)))
p.finished.connect(self.OnProcessFinished)
p.readyReadStandardOutput.connect(self._OnProcessOutput)
p.readyReadStandardError.connect(self._OnProcessError)
return p
@Slot()
def _OnProcessOutput(self):
'''
处理子进程标准输出
'''
if self.p != None:
data = self.p.readAllStandardOutput()
# 获取子进程的输出数据
data = bytes(data.data()).decode()
self.AppendLog(data)
# 根据自程序的输出获取子进程的执行进度
progress_value = progress_parser(data)
if progress_value != None:
self.progressBar.setValue(progress_value)
else:
warnings.warn("Invalid call")
@Slot()
def _OnProcessError(self):
'''
处理子进程标准错误
'''
if self.p != None:
data = self.p.readAllStandardError()
data = bytes(data.data()).decode()
self.AppendWarn(data)
else:
warnings.warn("Invalid call")
@Slot(str)
def AppendLog(self, text):
'''
插入一般日志
'''
self.teOutput.appendPlainText(text)
@Slot(str)
def AppendWarn(self, text):
'''
插入警告
'''
self.teOutput.appendHtml(f"<font color='red'>{text}</font><br>")
@Slot()
def OnExecuteProcess(self):
# 保证总是只有一个子进程, 每次运行相关方法时要检查子进程是否存在
if self.p == None:
self.AppendLog(f"Execute Start in {time.ctime()}")
# 将创建的子进程作为成员保存
self.p = self._CreateProcess(7)
self.p.start()
self.pbExecute.setEnabled(False)
self.pbTerminate.setEnabled(True)
else:
warnings.warn("Process has running")
@Slot()
def OnTerminateProcess(self):
if self.p != None:
self.AppendWarn(f"Execute Terminate")
self.p.kill()
else:
warnings.warn("Invalid call")
@Slot()
def OnProcessFinished(self):
self.AppendLog(f"Execute End in {time.ctime()}")
# 在子进程结束时, 销毁子进程对象
self.p = None
self.pbExecute.setEnabled(True)
self.pbTerminate.setEnabled(False)
self.progressBar.reset()
app = QApplication()
win = MainWin()
win.show()
app.exec()
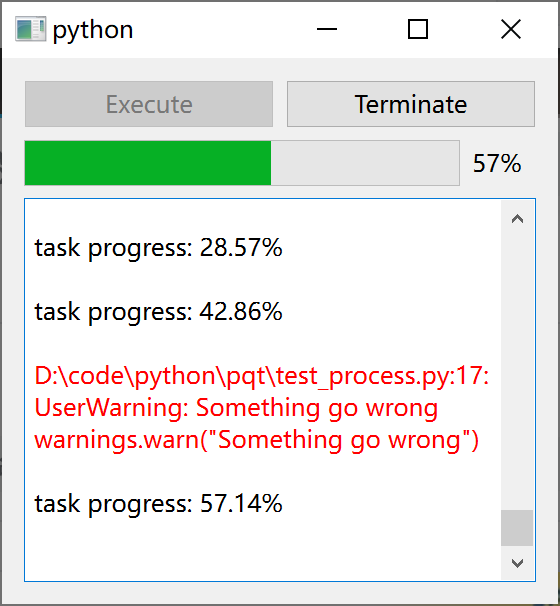
其中 test_process.py 程序
import time
import sys
import numpy
import warnings
def cout(text: str):
# sys.stdout.write(text)
# sys.stdout.flush()
print(text, flush = True)
def task(i, run_times):
cout(f"task progress: {i / run_times * 100:.2f}%")
time.sleep(0.3)
if i == 3:
warnings.warn("Something go wrong")
if __name__ == "__main__":
id = int(numpy.random.random() * 65536)
run_times = 1
try:
run_times = int(sys.argv[1])
except:
run_times = 1
cout(f"process {id} start in {time.ctime()}")
for i in range(run_times + 1):
task(i, run_times)
cout(f"process {id} exit in {time.ctime()}")
运行效果